In the decentralised world of cryptocurrency, there is no central authority. As it is based on blockchain technology, cryptocurrency involves financial account databases that are shared across a network and spread over various geographical locations.
This also means that if you forget your crypto wallet login details, there aren’t many places you can turn to. Blockchain analysis firm Chainanalysis estimates that about 3.7 million Bitcoins have been lost by owners. That is nearly 20% of the 18.9 million Bitcoins in circulation1.
That is why one of the most important things to look into when investing in cryptocurrency is how to store it. There are various storage options available, from hardware devices and applications to sheets of paper. To find out which is most suitable for you, you need to know the pros and cons of each option.

Different types of cryptocurrency wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets are where investors store their digital currency. Each wallet contains a seed from which pairs of private (secret) and public keys can be generated.
- The public key is like your personal address. You’ll need the public key to send cryptocurrency from your crypto exchange account to your own wallet. And anyone can send you cryptocurrencies, so long as they know your public key.
- On the other hand, the private key is like a login password. You’ll need the private key to sell or withdraw your crypto. Anyone who knows your private key has full access to your account.
Common types of cryptocurrency storage
There are three common types of cryptocurrency storage wallets — Hot, cold, and custodial wallets.
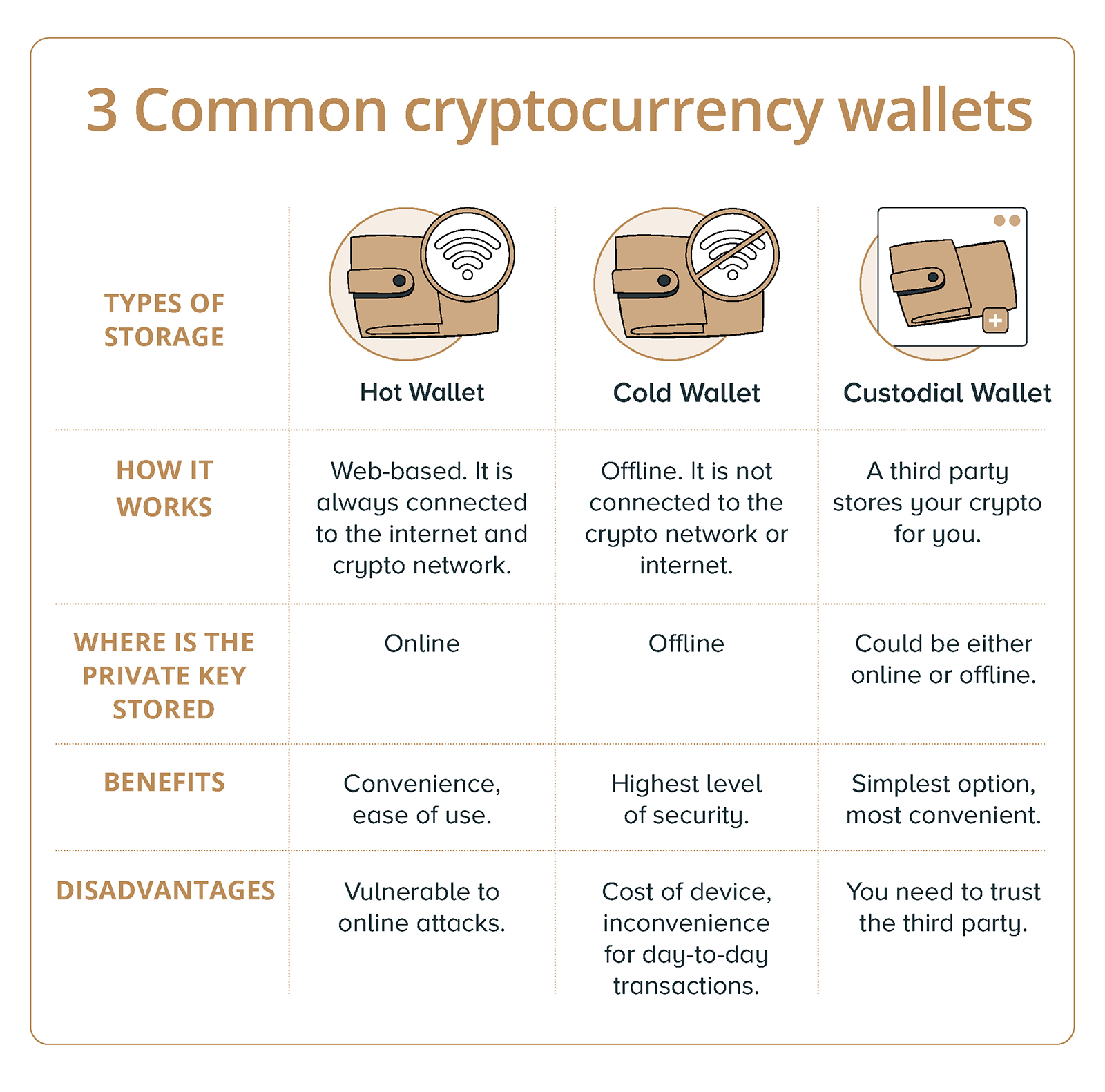

Hot wallets: Convenient but less secure
Hot wallets are easy to use and are almost always free. They are available as a desktop or mobile app and can also be web-based.
As hot wallets store your private keys online and are connected to the internet, the risk is that they can be hacked as the private keys are essentially stored online.
The integrity of a hot wallet depends heavily on the app’s security systems.
Therefore, it’s not a method you would want to use for storing significant amounts of cryptocurrency.

Cold wallets: Offline cryptocurrency storage
Cold wallets are not connected to the internet. Your private key is kept offline, typically in a plug-in hardware device, or a paper wallet. Cold wallets are often seen as the safest option for storing your cryptocurrency.
However, the main downsides are that it’s less convenient for day-to-day transactions, and the device or paper could get damaged or misplaced.
Cold wallet — Plug-in hardware devices
While hardware devices for cold wallets look like USB thumb drives, their sole purpose is to access cryptocurrency in a safe and secure manner.
Seed phrases (12 or 24 words) are generated when you first set up the wallet. As the device will only display these words once, you should back them up manually. This back-up is typically done on steel plate or paper. You will need to store the back-up securely as it is your only way to restore your wallet and its associated keys if the hardware is lost or damaged.
Private keys are stored in the hardware device. So when making a transaction, you just need to authenticate the trade via the hardware wallet. This protects your private key as the amount of time that it is connected online is limited. The moment you’ve authenticated the transaction, your key can be disconnected from the internet.
Hardware wallets have a few other disadvantages:
- Cold wallet devices cost about US$40 to US$1592, while hot wallets are usually free.
- Devices have a data storage limit. This affects the number of different types of cryptocurrency investors might want to store. The limit doesn’t affect the number of transactions or amount of a crypto stored.
- Potentially difficult for beginners to use as there are more steps to follow.

Storing cryptocurrency in a custodial wallet
Custodial wallets are wallet services offered by a cryptocurrency exchange, platform or custodian. Custodial wallets can utilise cold storage, hot storage, or a combination of the two.

Advantages of custodial wallets:
- Least amount of effort in keys management
- Easy to carry out a transaction
- Flexibility to transfer it to your own hot or cold wallet. However, do note that not every crypto or digital asset platform allows this.
When using a custodial wallet, you will need to trust the company running the platform because they are holding the private key for you.
A trusted custodian company would have: i) Sufficient security measures in place; ii) Demonstrated good risk management and iii) Good financial standing minimising their risk of going bankrupt.
For instance, DBS Bank carries the highest ratings from the biggest 3 credit rating agencies: S&P, Moody’s and Fitch. And DBS Digital Asset Custody, a service which is available to Accredited Investors, uses hierarchical storage management (HSM), which is an advanced and secure data management technique.

Storing cryptocurrency for the long-term
While there isn’t a hard and fast rule about how to store your cryptocurrency, a common best practice is to have both a hot and a cold wallet — The web-based or app-based hot wallet could be used for everyday transactions, and the cold wallet can be used to store the bulk of your cryptocurrency.
If convenience is a big factor, consider using custodial wallets that have a good track record and robust security infrastructure, as well as good financial standing.
Learn more about storing your cryptocurrency with DBS.
Sources:
1 BBC News. 10 February 2022. ‘Hackers helped me find my lost Bitcoin fortune’. https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-60318946
2 Software Testing Help. 16 July 2022. 8 best bitcoin hardware wallet review and comparison. https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/bitcoin-hardware-wallet/
Disclaimers and Important Notice
This article is for information only and should not be relied upon as financial advice. Any views, opinions or recommendation expressed in this article does not take into account the specific investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs of any particular person. Before making any decision to buy, sell or hold any investment or insurance product, you should seek advice from a financial adviser regarding its suitability. This article is not intended for distribution to, or use by, any person or entity in any jurisdiction or country where such distribution or use would be contrary to law or regulation.







